
 |
| [ Home ] [ Manage Datasets ]
[ Supplementary files ] [ User manual ] [ About ]
You are logged in as . [logout] |
|
1. Overview 2. Analysis modules 3. Motif & Expression 4. Expression & Expression 5. Motif & Function 6. microRNA search 7. Data upload |
mESAdb - motif & function |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Sequence motifs are important in classifying microRNAs. Motif & Function module helps associate a molecular, biological or cellular function with a group of miRNAs selected based on sequence characteristics. In detail, this module can be used to select miRNAs containing a particular motif ranging from dinucleotide sequence to seed consensus motifs. Upon selection of a group of microRNAs, the enrichment analysis of predicted target genes are performed for selected HUGE, KEGG and GO class.
In order to use this module, first you need to select any organism by clicking the radio buttons. Second, type a nucleotide motif up to 6 nucleotides in length into the text field or select a dinucleotide motif from the pull down menu. You can also upload your own microRNA list (see example text file) by using the "miRNA list upload" option. Finally, you can select the region that the nucleotide motif has to appear in by clicking radio buttons. |
||
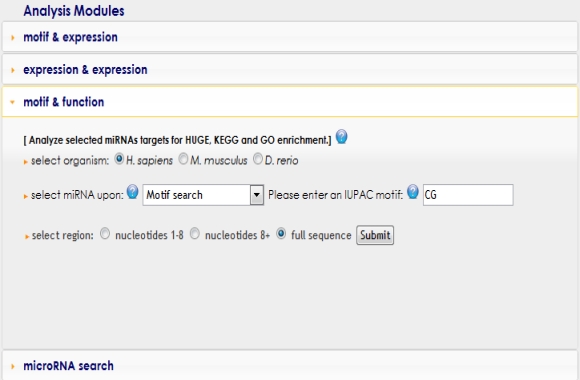
|
||
In the next page, the subset of microRNAs that meet the selection criteria are listed.
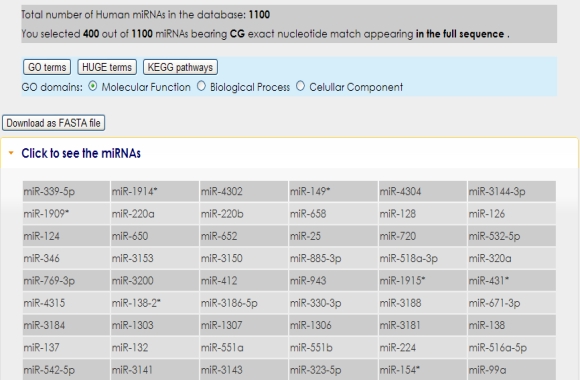 You can get information regarding predicted microRNA targets and related Gene Ontology terms of those targets by clicking on the microRNA name in question. 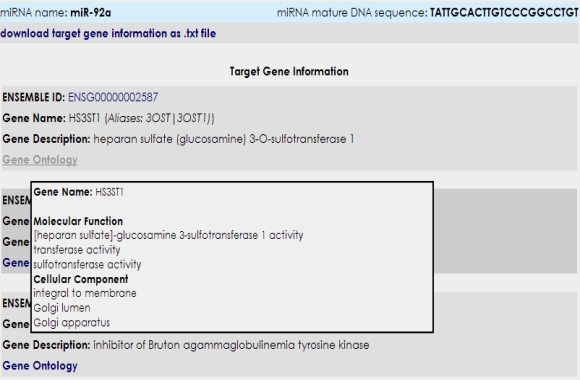 It is also possible to obtain related Gene Ontology, KEGG pathways and HUGE terms of microRNA subset targets with their probability values by clicking analysis buttons. However, HUGE analysis only works for human microRNA subsets. 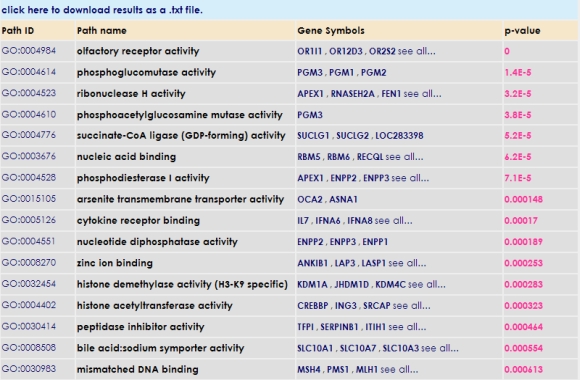 Additionally, you can download microRNA mature DNA sequences in FASTA format by clicking the download button. |
||
| [ Home ] [Manage Datasets] [ Supplementary files ] [ User manual ] [ About us ] [ Logout ][ HelpPoints Off] mESAdb was developed for and tested on Chrome, Firefox and Safari. Please use one of these browsers for the best experience. Copyright © 2010 Konu Lab - Bilkent University Additional copyright & license information. |